All locomotions are movement but all movement not locomotion.Types of movement:-
1) Pseudopodial/ amoeboid:- cyclosis (streaming movement of cytoplasm) e.g. Macrophage.
2) Ciliary:- e.g. Trachea and fallopian tubes.
3) Flaggelar:- e.g. Sperm
4) Muscular:-e.g. All body part movement.Skeletal Muscles:-
- These are voluntary muscles.
- Fascia is covering of connective tissue present beneath skin surrounding entire muscle.
- Muscle is made up of bundles of muscle cells called fascicle covered by perimysium.
- Many such bundles are covered with epimysium.
- Skeletal muscles are syncytial i.e. multinucleated due to the fusion of cells.
- It shows light and dark bands, therefore, called striated.
- The endoplasmic reticulum is called sarcoplasmic reticulum which stores calcium with protein calsequestrin.
- The plasma membrane is sarcolemma covered by endomysium.
- Invaginations in the plasma membrane are called T-tubules(Transverse tubules) which help in spreading signal deep inside the muscle. It is found near
the Zline and sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Muscle is made up of two types of myofilaments/ myofibrils present in parallelly arranged sarcomere.
Actin:-
- Light filament.
- The polymer of Globular actin( G- actin)
- G-actin joins to form F-actin (Filament actin).
- Two such filaments coil together to form Actin.
- Each F-actin has its own filament of tropomyosin (Regulatory protein).
- All regular interval Troponin (Regulatory protein) made up of 3 subunits are found.
- Three subunits of troponin:-
- Troponin for inhibition.
- Troponin for Tropomyosin.
- Troponin for calcium.
- Each G-actin has myosin binding site which is covered by tropomyosin and troponin at regular interval.
- Actin is surrounded by three myosins.
- One end of actin is free, others joined to the Z membrane.
- Diametre = 50 A.
- It forms a light band.
- Heavy filament.
- The polymer of meromyosin-II.
- Meromyosin has two parts
- Heavy meromyosin(HMM)
- Light meromyosin (LMM)
- Head has actin binding site at the tip and ATP binding site at sides.
- Centre of the head has ATPase activity.
- Diametre-100A.
- Free at both ends.
- Present in center of sarcomere.
- Each myosin is surrounded by 6 actin.
- Forms dark band.
- Given by Huxley and Huxley.
- Supported by Niedergerk and Hanson.
- ATP binds to head of myosin.
- ATPase activity of myosin converts ATP into ADP + Pi. This requires magnesium.
- Myosin forms cross the bridge with Actin and swirls towards the center of sarcomere.
- Actin filament slides over myosin causing contraction of sarcomere thus muscle.
- Calcium comes out from SR and binds to troponin. This removes tropomyosin and troponin complex away from myosin binding site of Actin.
- Myosin can now easily bind actin.
- Relaxation of muscle also requires ATP.
- When the new ATP binds to myosin ATP and Pi is removed. This shifts myosin back to its original site and sarcomere relaxes.
- Entry of calcium back into SR is against a concentration gradient. Therefore active transport also requires ATP.
A-band - Anisotropic
I-band - Isotropic
H-band - Hanson`s
Z-line - memb. of Krauz.
M-line - Middle line
- A-band never changes its size.
- I and H-bands reduce.
Muscle Twitch- Sudden spontaneous contraction followed by relaxation. It is found only in the laboratory.
Muscle Tetanization-Sequential recruitment of motor units to maintain contraction.
Muscle Tone- A very low level and sustained contraction of our back muscle to maintain posture.
All or none phenomena-There is a minimum threshold value of neurotransmitters required for the muscle to contraction below which muscle can`t contract. Any value above this threshold will cause the same amount of contraction. The strength of contraction depends upon the number of motor units working .
Rigor Mortis- Stiffening of the body after death due to depletion of ATP.
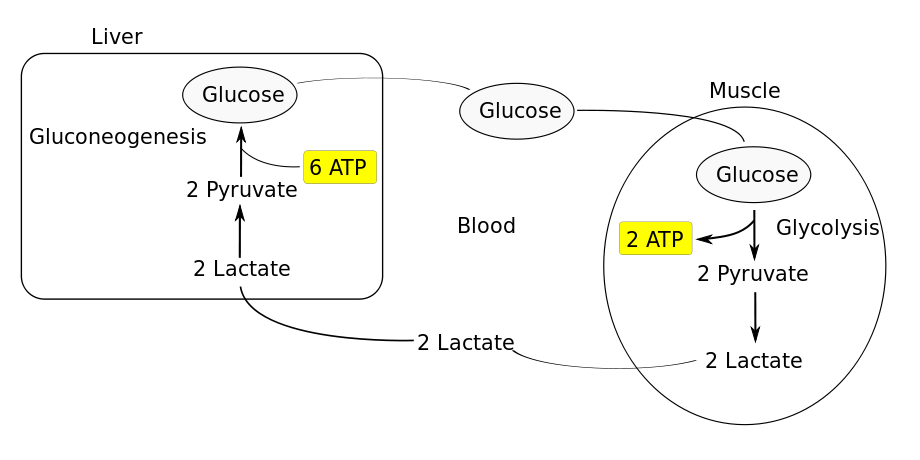
Cori Cycle-
Muscle Fatigue-Accumulation of lactic acid at neuromuscular junction causing pain and preventing contraction is called muscle fatigue.
Oxygen Debt- Additional oxygen required to remove all lactic acid formed during exercise is called oxygen debt. Breathing rate, therefore, remains high for some time after exercise.
Summation-Many sub-threshold signal, when given in a quick manner, adds up to cross a threshold value.
Difference between Red muscle fibres and white muscle fibres-
Red muscle fibres White muscle fibres
-Tonic muscle -Twitch muscle.
-High myoglobin . -Less myoglobin.
-High mitochondria - Less mitochondria
-Aerobic respiration - Anaerobic respiration
-No fatigue -Fatigue
-Slow and sustained contraction - Quick and short duration contraction
-Less ER - Many ER
e.g. back extensor muscle, flight -e.g. eye muscle, flight muscle of crow etc.
muscle of migratory birds
Antagonistic muscle:-
Each part is supplied with a pair of antagonist's muscles with opposite action.
2) Abductor - moves the arm away from the body. e.g. Deltodius.
Adductor- Moves arm towards the body. e.g. Latisimus dorsi.
3) Depressor- Moves jaw below e.g. Depressor mandibuli
Elevator - Moves jaw up e.g. Massetor
4)Sphinctor
Dilator
5) Supinator- Moves palm/sole anterior / up
Pronator- Moves palm/sole posterior/ down.
Oxygen Debt- Additional oxygen required to remove all lactic acid formed during exercise is called oxygen debt. Breathing rate, therefore, remains high for some time after exercise.
Summation-Many sub-threshold signal, when given in a quick manner, adds up to cross a threshold value.
Difference between Red muscle fibres and white muscle fibres-
Red muscle fibres White muscle fibres
-Tonic muscle -Twitch muscle.
-High myoglobin . -Less myoglobin.
-High mitochondria - Less mitochondria
-Aerobic respiration - Anaerobic respiration
-No fatigue -Fatigue
-Slow and sustained contraction - Quick and short duration contraction
-Less ER - Many ER
e.g. back extensor muscle, flight -e.g. eye muscle, flight muscle of crow etc.
muscle of migratory birds
Antagonistic muscle:-
Each part is supplied with a pair of antagonist's muscles with opposite action.
1) Flexor - Bends e.g. Biceps.
Extensor -extends e.g. Triceps.2) Abductor - moves the arm away from the body. e.g. Deltodius.
Adductor- Moves arm towards the body. e.g. Latisimus dorsi.
3) Depressor- Moves jaw below e.g. Depressor mandibuli
Elevator - Moves jaw up e.g. Massetor
4)Sphinctor
Dilator
5) Supinator- Moves palm/sole anterior / up
Pronator- Moves palm/sole posterior/ down.




No comments:
Post a Comment