- Porifera means pore bearing ( Porous-pore ; ferre - bearing )
- phylum porifera genrally consists sponges.
- Sponges were first recognised as animals by John Ellis(1765).
- In 1825 Robert Grant gave the name Porifera.
- About 5000 species of sponges are known till now.
- Habitat- Aquatic, mostly marine ,rarely fresh water (e.g., spongilla) , solitary or colonial, sessile . Sponges are mainly found in warm water.
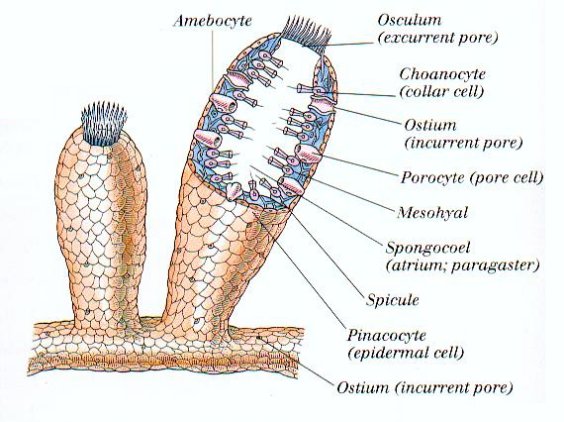
- Body form- body is porous. pores are of two types : inhalent pores- ostia and exhalent pores- Oscula.
- Symmetry- Mostly asymmetrical. Some shows radial symmetry.
- Germ layers- Sponges are first multicellular diploblastic animals i.e., derived from two germ layers ectoderm and endoderm.
- Level of organisation - have cellular level of organisation.
- Body wall- Body wall of common sponge consists of three layers.
A) Pinacoderm( dermal layer) - Outer cellular layer consisting pinacocytes and porocytes.
B) Choanoderm( gastral layer) - Inner cellular layer which consists of highly specialised cells called choanocytes or collar cells.
C) Mesohyl layer ( Mesenchyme)- Non-cellular layer found inbetween pinacoderm and choanoderm. It has fine dispersed spongin fibres, spicules and amoebocytes.
7. Canal System- Three types of canal system are found in sponges: (i) Ascanoid canal system- simplest type found in Leucosolenia and few other sponges. (ii) Syconoid canal system- More complex then Ascon type. found in Sycon and some other sponges. (iii) Leuconoid canal system- most complex canal system found in spongilla.
Central body cavity of a sponge is called spongocoel or paragastric cavity.
The canal system helps the sponge in nutrition, respiration , exretion and reproduction.
8. Skeleton- Almost all sponges possess an internal skeletal system. It may consist of calcereous spicules or fine spongin fibres or of both , located in the mesohyl layer.
9. Digestion- intacellular and takes place inside food vacuoles.
10. Circulation- Distribution of food from the ingesting cells to the others is brought about by the wandering amoebocytes of mesohyl layer.
11. Respiration-exchange of gases by diffusion through the plasma membranes of the cells .
12. Excretion- By diffusion through the plasma membrane of cells. Chief excretory product is Ammonia.
13. Reproduction- Both sexual and asexual type of reproduction occurs. Asexual reproduction takes place by budding and gemmules. Sponges are hermaphrodite. Fertilization is internal.
14. Development- Zygote undergoes holoblastic cleavage. Development includes a free swimming larva, the amphiblastula( in sycon ) or parenchymula ( In Leucosolenia ) for dispersal of the species.
Unique features of phylum porifera-
Presence of Ostia and oscula , canal system and skeleton system made up of spongin fibres and spicules.
Classification
On the basis of skeleton, phylum Porifera is divided into three classes-
Class 1- Calcarea ( calcis= lime ) -The skeleton is of calcerous spicules.Examples;- Leucosolenia, sycon, grantia.
Class 2 - Hexactinellida ( hexa - six ). The skeleton is of siliceous spicules which have six rays. Ex.- euplectella, hyalonema.
Class 3- Demospongiae ( demas- frame ) - The skeleton is of spongin fibres with siliceous spicules or may be absent. Ex;- euspongia , spongilla, cliona, chalina.
Classification
On the basis of skeleton, phylum Porifera is divided into three classes-
Class 1- Calcarea ( calcis= lime ) -The skeleton is of calcerous spicules.Examples;- Leucosolenia, sycon, grantia.
Class 2 - Hexactinellida ( hexa - six ). The skeleton is of siliceous spicules which have six rays. Ex.- euplectella, hyalonema.
Class 3- Demospongiae ( demas- frame ) - The skeleton is of spongin fibres with siliceous spicules or may be absent. Ex;- euspongia , spongilla, cliona, chalina.
- Leucosolenia- simplest colonial sponge consisting of a number of horizontal and vertical tubes. The development is with a larva, the parenchymula.
- Sycon ( Scypha)- development is with a larva, the amphiblastula.
- Euplectella( The Venus flower basket) - found in deep sea water. They are abundent near the Phillipine Island and West Indies. Its skeleton is costly marriage gift in Japan as it is thought to be symbol of union of wife and husband.
- Hyalonema( The glass rope sponge) - It is fixed in the mud by a root tuft of long, twisted spicules. The upper surface has the gastral cone which bears opening of the excurrent canals.
- Euspongia - the bath sponge - surface is raised into small projections, called connules. Depressions between connules bears small pores , the dermal ostia. Its skeleton is used for bathing, washing automobiles, cleaning furniture and window panes. It is used for applying cosmetics, mopping etc.
- Spongilla- fresh water sponge-Spongilla a common, widely distributed fresh water sponge shows various shades of green colour because of the symbiotic algae present inside.
- Cliona - the boring sponge - The sponge can penetrate the rocks and break them into pieces . The sponge can also bore through the oyester shell and, therefore, harmful for pearl oyester industry.
- Chalina - the deadman`s fingers or the Meramaid`s gloves- It is shaped like a hand with several fingers perforated with oscula hence called so.

No comments:
Post a Comment